ANALYTICAL GEOCHEMISTRY Sub-Division
The Geochemistry laboratories are equipped with a wide range of modern facilities and instruments to provide analytical services to a wide range of clientele. The services offered include:
Sample Preparation
This is the process by which the samples are prepared for analysis. The Geochemistry laboratories offers facilities for different
types of sample preparation, such as weighing, screening, splitting, crushing, pulverizing, rock and core cutting, polishing of rock slabs,
preparation of thin sections, heavy mineral separation, acid digestion, preparation of pressed powder pellets and fusion glass beads, and
ashing/burning tests of some geological material. The sample preparation facilities are mainly utilised by researchers and clients in the
exploration and mining industries.
The choice of sample preparation method depend on the type of sample and the selected analytical technique. Good sample preparation practice
is essential to obtaining meaningful and reliable results.
A critical issue in analytical chemistry which should always be avoided or minimised during sample preparation is contamination. There
are many stages of sample preparation at which contamination may occur, for example, the choice of crushing or grinding equipment used may
contaminate the sample. The level of contamination depends on the sample hardness, crushing and grinding times as well as crushing/grinding
media. In order to minimise levels of contamination during sample preparation, carefully selected crushing and grinding tools with very
little contamination levels are used (e.g. agate grinding vessels).
Geochemical Analysis & Mineral Identification
Geochemical analysis and mineralogical services are accomplished with the use of some of the most sophisticated analytical instruments,
such as ICP-OES, AAS, XRF and XRD. A variety of techniques may be used, depending on the client's needs.
Other available instruments include, optical polarizing microscopes and binocular microscopes, some of which are fitted with cameras to aid
petrographic studies. Specialized gemmological instruments are available for identification and evaluation of gemstones.
Calibrations of these instruments are based on the analysis of international certified reference materials (CRM).
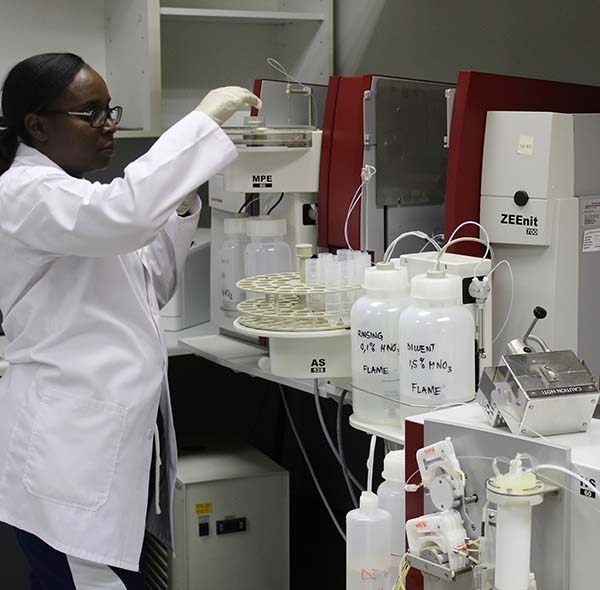
Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS)
The AAS lab is equipped with the Analytik Jena ZEEnit 700, a compact spectrophotometer providing Flame AAS, Graphite Furnace AAS and
Hydride AAS. The choice of digestion method depends on the elements of interest.

Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)
The ICP lab is equipped with the PerkinElmer Optima 7300 DV Spectrometer, which is used for multi-element analysis at varying
concentrations (major oxides to trace elements). Various sample digestion methods are applied depending on the elements of interest.

X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF)
- The Geochemistry labs are equipped with both the wavelength dispersive XRF (WD-XRF) and the energy dispersive XRF (ED-XRF) techniques.
- The WD-XRF is a Bruker S8 Tiger, used for analysis of a wide-range of elements from major oxides to trace elements. Fused beads and
pressed pellets are prepared for analysis using this technique.
- A portable Niton Xlt ED-XRF is routinely used for semi-quantitative analysis of rock specimen or powdered samples.

X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD)
The XRD lab is equipped with a Bruker AXS D8 Advance which is used for accurate identification of minerals. A wide range of minerals
(including gemstones and clay minerals) can be identified using this technique. Sample preparation involves grinding a representative portion of a sample.